WLTP Explained
How range, consumption and efficiency are measured.

The WLTP is a global vehicle testing system that predicts fuel economy, emissions, and electric vehicle range.
What is WLTP Range?
WLTP range is the maximum distance an EV will travel on a single charge, based on a standardised test.
The range is calculated by running the test cycle (WLTC) twice and measuring energy consumption from the battery’s available capacity.
WLTP City Range
A few manufacturers list "City Range." The city calculation is from the WLTP test cycle, where only the Low and Medium phases are used.
The city range applies to very few situations. You would have to be driving under 60 km/h all the time.
WLTP Combined Range
WLTP combined range is the range calculated from the low-speed (city) AND high-speed (highway) test phases.
This is a complete calculation using the 4-phase test cycle rather than just the low and medium cycles.
Where a manufacturer lists "WLTP range", - they mean WLTP combined range.
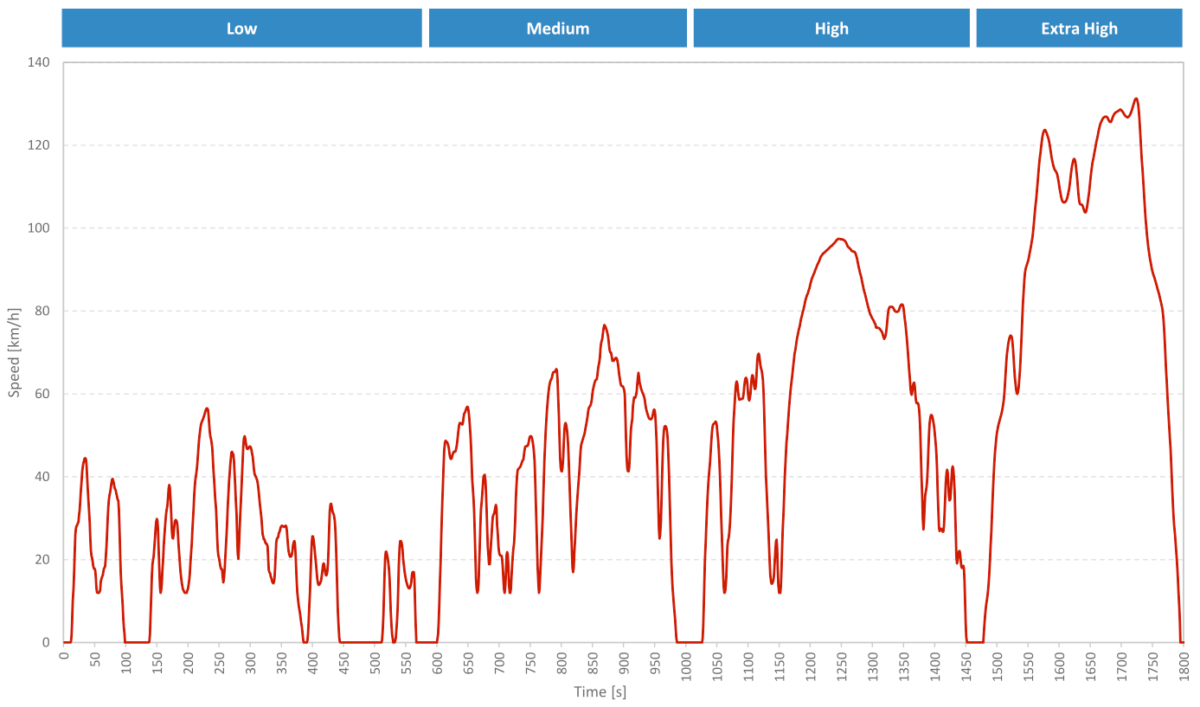
What is the WLTP cycle?
The WLTP test cycle (WLTC) consists of a series of starts, accelerations, and stops in a controlled environment over a set period of time.
The test is carried out at an ambient temperature of 23°.
The 30-minute cycle is split into 4 phases, named after their respective maximum speeds:
| Max Speed (km/h) | Average Speed (km/h) | Duration | |
| Low | 56.5 | 25.7 | 9:49 |
| Medium | 76.6 | 44.5 | 7:13 |
| High | 97.4 | 60.8 | 7:35 |
| Extra High | 131.3 | 94 | 5:23 |
The average speed of the cycle is 46.5 km/h.
WLTP Consumption or Driving Efficiency?
The WLTP measures electric energy consumption. This is called efficiency or rated consumption.
However, you can also see efficiency readings on your vehicle's dashboard.
What you see on your vehicle's dashboard is not WLTP consumption.
-
WLTP consumption is expressed as Wh/km and is based on "recharged electric energy from the mains."
-
Dashboard or driving efficiency is expressed as kWh/100 km or km/kWh and is measured by the vehicle from electric energy stored in the battery.
Many websites and online publications mix the two up.
WLTP-rated consumption includes charging loss
-
WLTP performs a battery recharge as part of its test, so consumption includes charging losses.
-
WLTP consumption allows drivers to compare energy costs (like litres per 100 km in a petrol car).
-
Electricity 'lost' during charging is typically between 7-12% (worse in cold weather).
-
In some cars, electricity from charging can be used to heat (or cool) the battery.
Dashboard efficiency does not include charging loss
-
The consumption you see on your dashboard does NOT include charging losses.
-
It measures the vehicle's efficiency (weight, powertrain, aerodynamics) and your driving conditions.
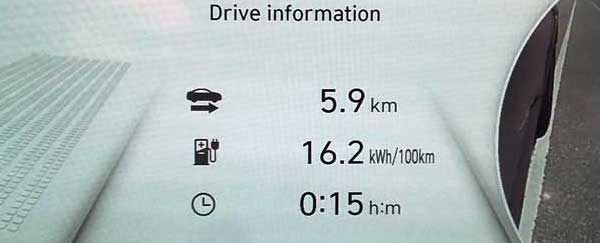
IONIQ 5 dashboard efficiency - 16.2 kWh of battery energy used per 100 km
Driving consumption can be estimated by dividing the usable battery capacity by the WLTP range.
Efficiency differences in EVs with similar Range and Battery
Consider three fictional EVs with matching gross battery capacity and range.
| Fictional EV | Sparky McPlug-in | Shock-Mobile 250 | Electra GT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery | 60 kWh | 60 kWh | 60 kWh |
| Usable | 57 kWh | 57 kWh | 58 kWh |
| Range | 400 km | 400 km | 400 km |
| Charging loss | 10% | 12% | 10% |
You might assume they would have the same efficiency.
-
The most efficient is the Sparky McPlug-in. It uses the least amount of mains electricity to travel its 400 km.
-
The Shock-mobile needs more electricity to fill its battery due to a higher charging loss.
-
The Electra GT is the least efficient. It has more usable capacity and, therefore, needs more recharging.
The only metric that can compare these is WLTP consumption.
What is real-world range?
The so-called 'real-world' range is not an official measure.
-
Our actual or real range will differ because none of us drives in WLTP test cycles.
-
Some of us do mostly highway driving, and some primarily do urban driving. Which is "real"?
The WLTP cycle is poor at estimating motorway driving and cold-weather driving.
It's conducted at 23° - not something you'll see in winter. Neither the heater nor the air conditioning system is used during a WLTP test.
Cold temperatures, fast speeds, and wind will all lower range.
Has anyone tested the real-world range?
Yes. In Norway, enthusiasts routinely test the range of many EVs.
These findings show:
In a Norwegian winter (0° to -10°), the vehicles have a 10-23% lower range than WLTP. However, every year this test is run (with new EVs) the results are getting better and better.
Remember that WLTP is undertaken at 23°, so the nearer your locality is to that temperature, the more accurate the WLTP range will be.
Can you rely on real-world range?
All references to real-world range are estimates. They are not based on a scientific test but can be helpful.
What are TEH and TEL (Vehicle H and Vehicle L)?
Sometimes referred to as Test Energy Low or Vehicle Low, this has nothing to do with the low or high phases in the test cycle.
Different variants or trims may alter range and energy consumption within a vehicle model family. The WLTP takes that into account (in conjunction with the manufacturer).
Many things can affect range: tyre rolling resistance, changes to body trim might affect aerodynamics, and other add-ons might add weight.
-
Vehicle H (energy high) refers to the model trim with the highest energy demand,
-
Vehicle L (energy low) is the model trim with the lowest energy demand.
Which range is the manufacturer listing? They should list the range and consumption figures matching the vehicle trim being sold.
Have all vehicles been through the WLTP cycle?
No. WLTP only became law in Europe in 2017, using the NEDC cycle before that. In this situation, the WLTP range is estimated.
The USA uses a different test (EPA), while China uses its test cycle (CLTC).
CLTC vs. WLTP
The China Light-Duty Vehicle Test Cycle (CLTC) is considerably more optimistic than the WLTP.
Designed for Chinese conditions and driving habits, it has only 3 phases (and lacks the extra high phase that the WLTP has).
CLTC to WLTP Conversion Factor: 0.82
Conversion formulas are a blunt tool but helpful. Consider the range specs of the following Chinese-manufactured vehicles:
| Actual data | NEDC | CLTC | WLTP |
|---|---|---|---|
| BYD Atto 3 | 480 km | 510 km | 420 km |
| BYD Dolphin | 420 km | 340 km |
EPA vs. WLTP
The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) test combines a highway test (short, high-speed test - the HWFET) with an urban driving cycle (UDDS). The result is then multiplied by 0.7 to get a more realistic figure.
| Actual data | EPA | WLTP |
|---|---|---|
| Hyundai Kona (2020) | 258 miles | 484 km |
| Nissan Leaf 40 kWh (2020) | 150 miles | 270 km |
| Volkswagen ID.4 Pro (2023) | 275 miles | 519 km |
EPA (miles) to WLTP (kilometres) Conversion Factor: 1.88
This converts to kms, and applies an EPA to WLTP conversion factor of 1.16
Example: 275 miles (EPA) × 1.88 = 517 km (WLTP)
NEDC vs. WLTP
The New European Driving Cycle (NEDC), is not new anymore. Developed in the 1970s, it has been superseded by the WLTP.
The NEDC has a simple 20-minute test cycle, most of which is at 50 km/h or under. For EV range, NEDC is far more generous than WLTP.
NEDC to WLTP conversion factor: 0.85
Example: 535 km (NEDC) × 0.85 = 444 km (WLTP)
ARAI vs. WLTP
India uses the ARAI to test EV range. The cycle used for passenger vehicles (such as SUVs and sedans) is the modified Indian Drive Cycle. This has a max. speed of 90 km/h and an average of 50 km/h - it is similar to NEDC.
ARAI to WLTP conversion factor: 0.81
Example: BYD Atto 3 - 521 km (ARAI) x 0.81 = ~420 km (WLTP)
What is 3P-WLTP?
3P-WLTP means three-phase WLTP, using only data from the first three phases of the test cycle.
However, this only applies to emissions data, and all fully electric vehicles are assigned a value of zero emissions. WLTP range is listed (by both the manufacturer and on the vehicle label) using 4P-WLTP (i.e. the complete cycle).
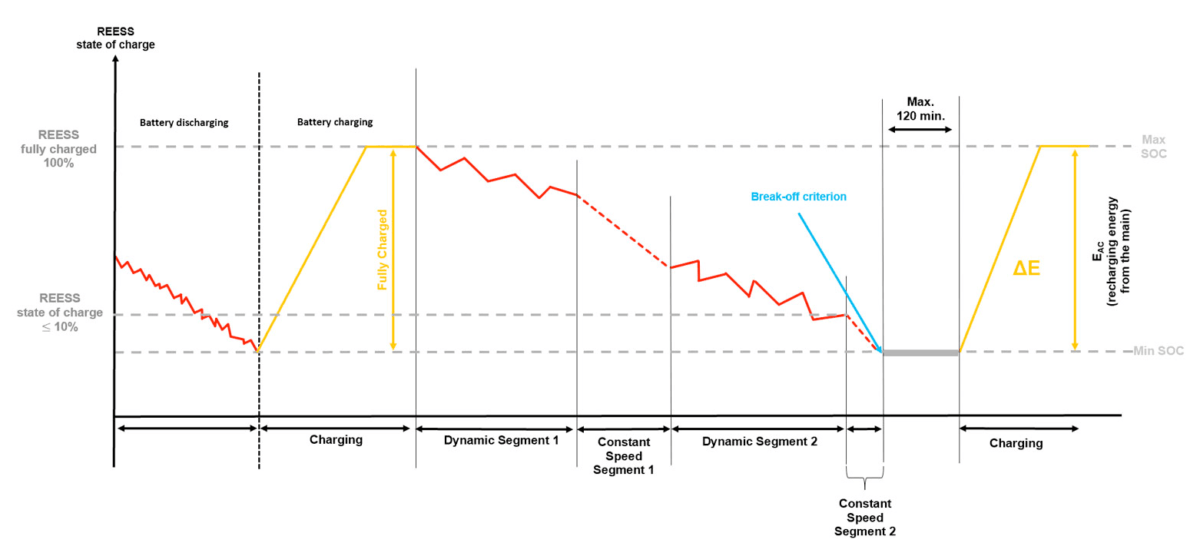
WLTP Test Cycle Outline
The complete test for an electric vehicle consists of the following phases:
-
Start at full battery.
-
Dynamic Segment 1: Drive the 4-phase cycle, followed by a 2-phase low-medium cycle (city).
-
Drive at 100 km/h for a period of time.
-
Dynamic Segment 2: Drive the 4-phase cycle, followed by a 2-phase low-medium cycle (city).
-
Drive at 100 km/h until battery depletion.
-
Recharge the battery to 100%.
During the test, the electrical current and voltage pulled from the battery are measured (p. 744).
The WLTP mentions, "the manufacturer may use the on-board current measurement data. The accuracy of these data shall be demonstrated to the approval authority."
These measurements are kept from the start of the test until the end (break-off).
During the recharge, measuring equipment is placed between the charger and the mains to measure recharged electric energy.
How is electric range calculated? (p. 767)
Electric range (km) = usable battery energy (determined by measuring consumption until break-off (Wh) / electric energy consumption (Wh / km).
Electric energy consumption (EC) is calculated by:
EC (Wh/km) = electric energy change during cycle period (Wh) / distance travelled (km).
Where energy change = (voltage x current over time) / 3600 (to give Wh).
How is WLTP consumption calculated? (p. 764)
The WLTP refers to this as electric energy consumption, but with a different definition: "Electric energy consumption of the applicable WLTP test cycle based on the recharged electric energy from the mains and the pure electric range".
It's very confusing that "energy consumption" refers to recharged energy OR energy directly from the battery.
Efficiency (Wh/km) = Recharged electric energy from the mains (Wh) / Electric range (km).
Complete example
Sparky McPlugin is placed on the dynamometer with a full charge. The driver follows the test cycle and determines that the EV uses 6,090 Wh over 42 kilometres, so the battery consumption is 145 Wh / km.
The battery is depleted and then recharged back to 100%. The total energy depleted from the battery is 57,000 Wh. The total energy used to recharge is 63,450 Wh (about 6,000 Wh of charging loss).
Electric range is 57,000 Wh / 145 Wh per km = 393 km.
WLTP rated comnsumption is 63,450 Wh / 393 km = 161 Wh / km.
WLTP for PHEVs
WLTP testing of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEV) is complex.
The test includes:
-
Charge-depleting (CD) test - starts at a fully-charged battery, run the WLTC repeatedly until battery is empty.
-
Charge-sustaining (CS) test - starts when the battery is depleted (i.e. when the combustion engine kicks in and the vehicle is running in typical hybrid mode).
The test results are averaged, and a Utility Factor applied (a formula that presumes the percentage the car is driven in electric-only mode).
Comprehensive real-world testing has found the WLTP test to be very inaccurate and PHEVs typically consume about 3.5 times as much fuel as suggested.
-
PHEVs are charged less often than assumed.
-
They are driven for much longer journeys than assumed.
-
Company PHEVs, in particular, are using significantly more fuel (and emissions) than the WLTP.
-
Privately owned vehicles were used in electric mode for 45% to 49% of their driving.
-
For company-owned vehicles, the average was only 11% to 15%.
This has lead to an update of the Utility Factor (will be implemented over time).
Quick take: If a PHEV has WLTP consumption of 1.6L / 100 km - it's probably closer to 6L / 100 km. Over the next 5 years, newer PHEVs will begin showing much higher consumption figures.
— Research and writing by James Foster
References
-
The complete WLTP standard (all 839 pages of it). A great read if you have trouble sleeping.
-
"A test vehicle (vehicle H) with the combination of road load relevant characteristics (i.e. mass, aerodynamic drag and tyre rolling resistance) producing the highest cycle energy demand shall be selected from the family" p. 571
-
WLTP: Worldwide Harmonised Light Vehicle Test Procedure
-
Vehicle classes - almost all EVs fall into the Class 3b category (i.e., they can go faster than 120 km/h).
-
Conversion factor consulting report (PDF).
-
PHEV utility factors (the actual formula, implemented from 2025 onwards).